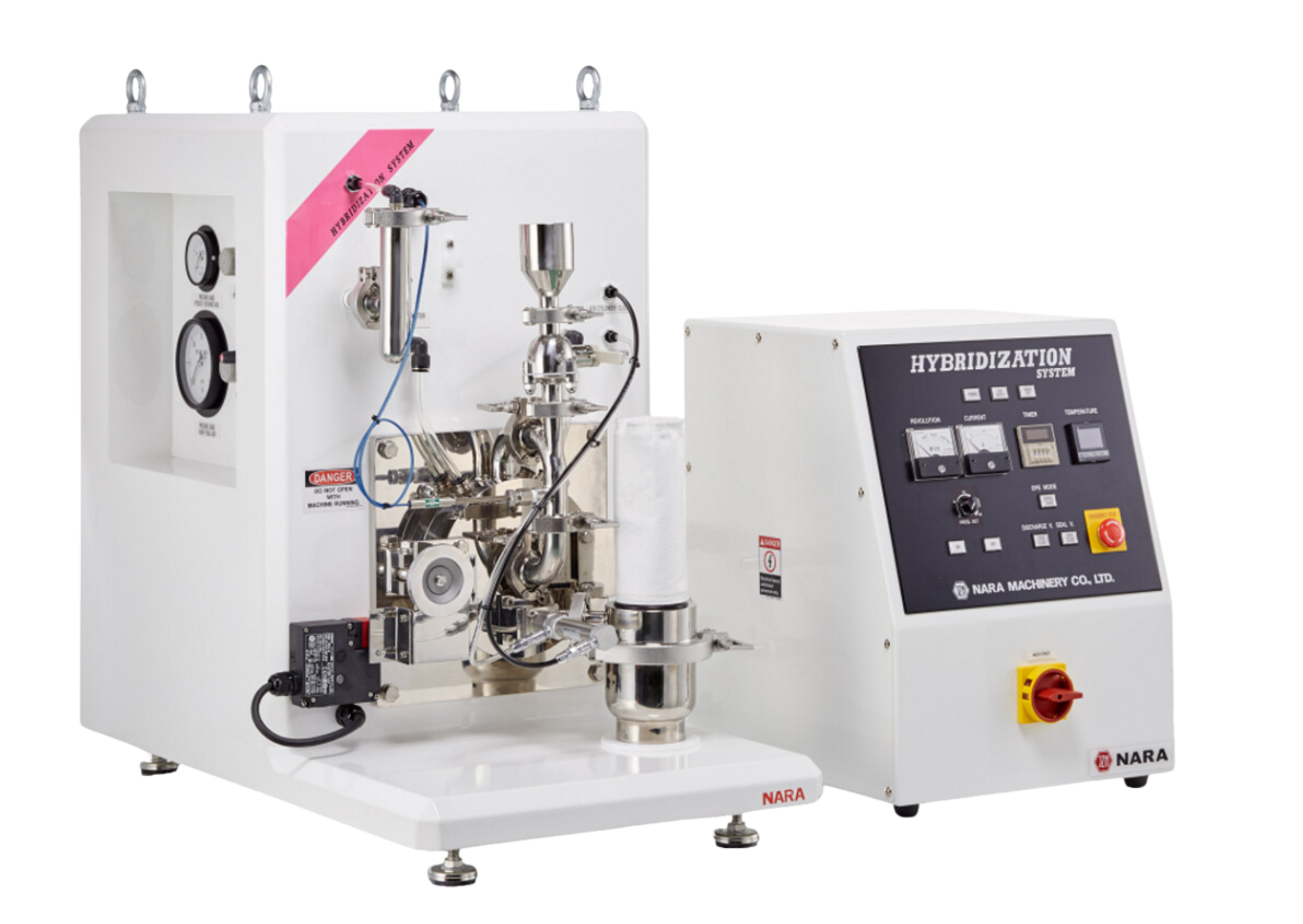
NARA Hybridization System (NHS)
Optimizing particle features
The NARA Hybridization System (NHS) is a technology for surface modification, preparation of composite materials of fine particles and precise mixing in a dry powder process. The raw material is dispersed in a high-speed air flow and processed by mechanical impact and shear forces. As a result, the raw material processing is not restricted by chemical laws.
The surface modification can be achieved by the following different methods:
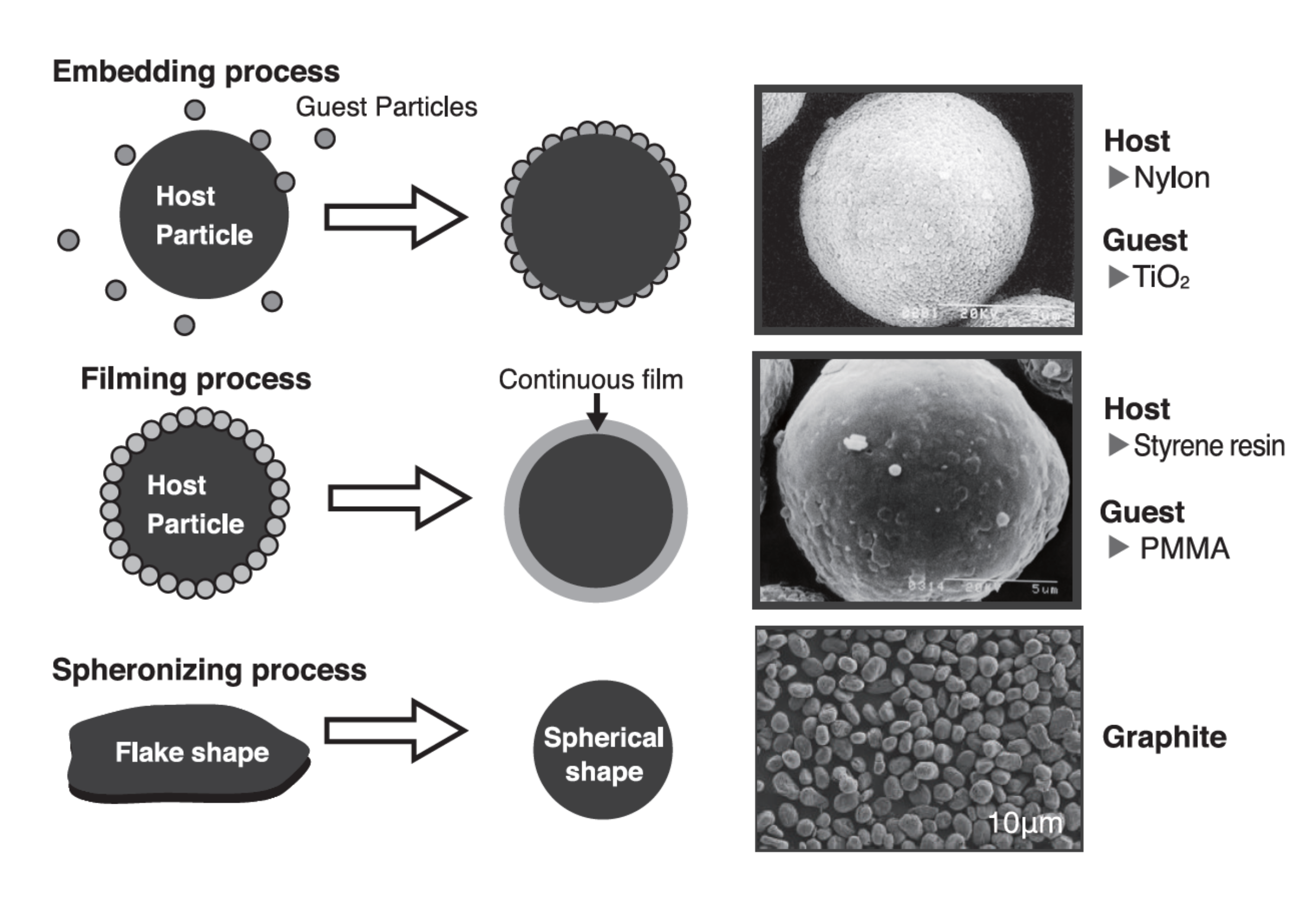
Spheronization (Rounding), embedding, penetrating and coating/filming (micro encapsulation). During hybridization process fine particles are applied onto or on the surface of a core particle.
By employing these methods of surface modification or formulation of powder composites, the NHS process has the ability to enhance conventional materials or even create new ones.
Types of Surface Modification
Embedding
Fine particles penetrate the surface of the core material.
Filming
Fine particles are plastically deformed – resulting in a complete coating of the core material.
Spheronization / Rounding
Raw material processing in the hybridization system achieves spheronized / rounded particles.
Advantages
- Improvement of dispersion, fluidization, wettability, electric or magnetic properties, catalytic properties, colour, weather resistance, light resistance, solubility, sintering properties, surface structure control, protection of reactions, controlled release, etc.
- High versatility since the combination of powder materials are infinite.
- Excellent dispersion of particles since the particles are processed in a high-speed air flow.
- Closed system with inert gas is possible to prevent oxidization of materials, for example metal fine particles.
- Solvent-free, dry powder coating process
Applications
- Battery materials
- Toner
- Luminescent materials
- Pharmaceuticals
- Food
- Paints
- Pigments
- Catalysts
- Cosmetics
- Electro ceramics
- Polishing materials
- Magnetic materials
- Biomaterials
- Optical materials
Application Examples – Spheronization of Anode Material
The NHS can achieve significant results in the spheronization of graphite as one of the commonly used anode materials improving both the bulk density and flowability.

Before and After Graphite Processing
Technical Data
| Type | NHS-0 | NHS-1 | NHS-2 | NHS-3 | NHS-4 | NHS-5 |
| Power [kW] | 2.2 | 11 | 22 | 45 | 90 | 185 |
| Powder amount [g/batch] | 50 | 400 | 800 | 1600 | 3200 | 6400 |
| Rotor diameter [mm] | 118 | 230 | 330 | 470 | 670 | 948 |
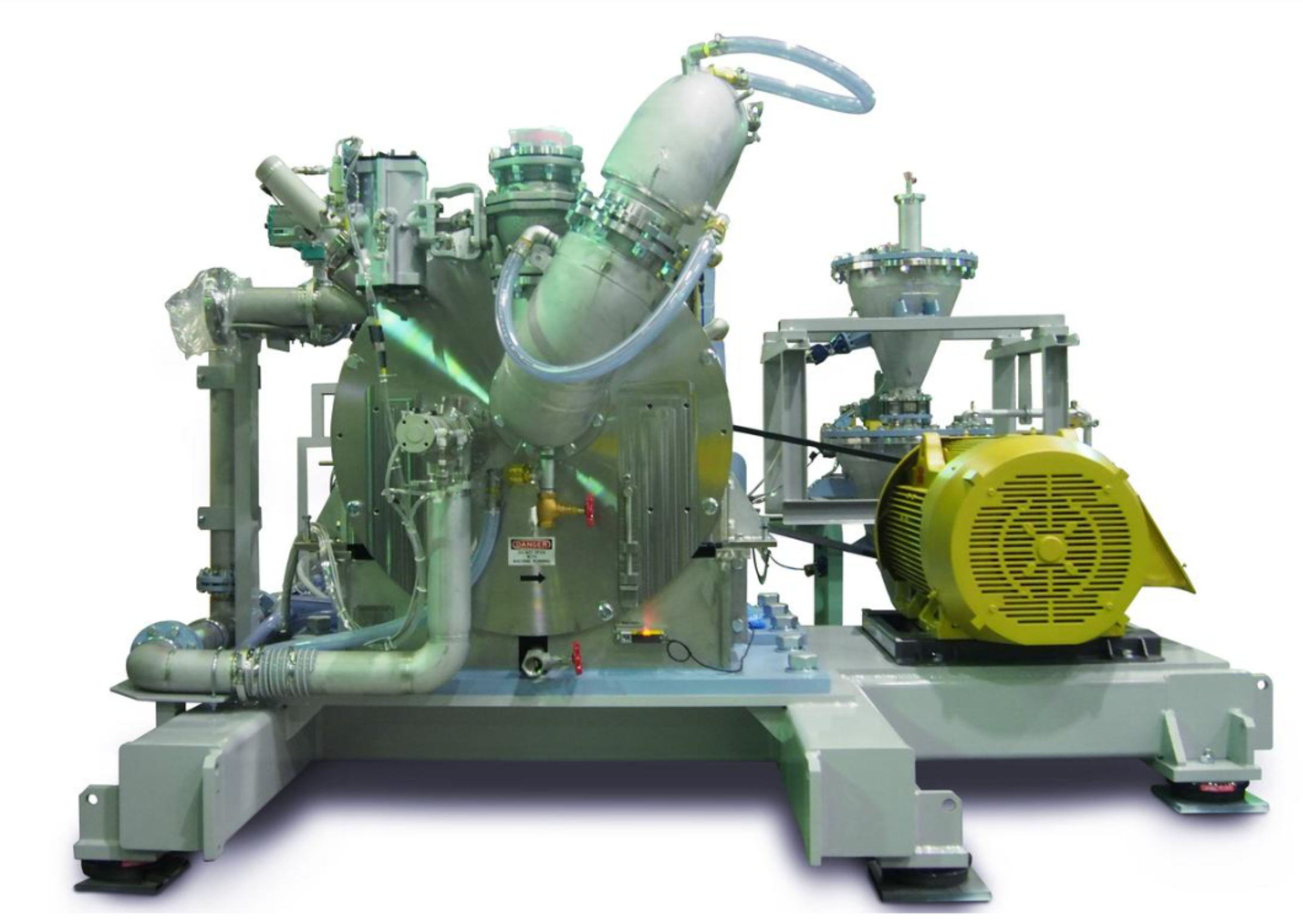

NHS-5 for Production
We are happy to manufacture according to your requirements.
Contact
Our team can support you with price information, product information and live demonstrations.
frankfurt@djkeurope.com
Phone: +49 6196 77614-11
Fax: +49 6196 77614-19